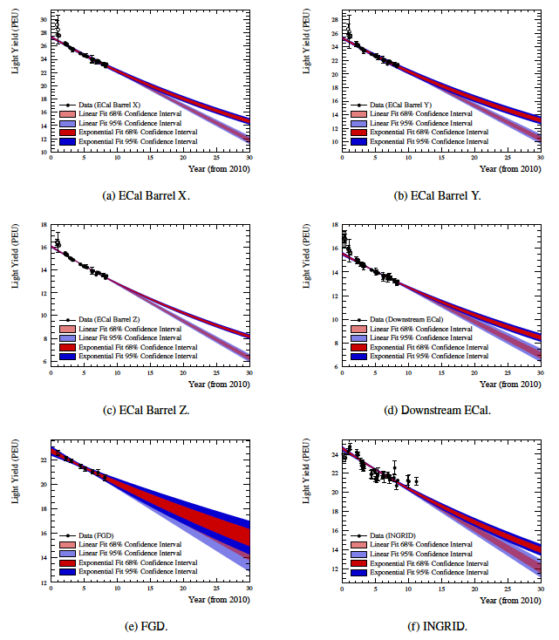
Scintillator ageing of the T2K near detectors from 2010 to 2021
The T2K experiment widely uses plastic scintillator as a target for neutrino interactions and an active medium for the measurement of charged particles produced in neutrino interactions at its near detector complex. Over 10 years of operation the measured light yield recorded by the scintillator based subsystems has been observed to degrade by 0.9–2.2\% per year. Extrapolation of the degradation rate through to 2040 indicates the recorded light yield should remain above the lower threshold used by the current reconstruction algorithms for all subsystems. This will allow the near detectors to continue contributing to important physics measurements during the T2K-II and Hyper-Kamiokande eras. Additionally, work to disentangle the degradation of the plastic scintillator and wavelength shifting fibres shows that the reduction in light yield can be attributed to the ageing of the plastic scintillator.
arXiv preprint: https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.12982
Data release: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6783269
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-0221/17/10/P10028
Reference: JINST 17 (2022) 10, P10028
The Electromagnetic Calorimeter for the T2K Near Detector ND280

A key element of the T2K near detector is the ND280 electromagnetic calorimeter (ECal), consisting of active scintillator bars sandwiched between lead sheets and read outwith multi-pixel photon counters (MPPCs). The ECal is vital to the reconstruction of neutral particles, and the identification of charged particle species. The ECal surrounds the Pi-0 detector (P0D) and the tracking region of the ND280, and is enclosed in the former UA1/NOMAD dipole magnet. This paper describes the design, construction and assembly of the ECal, as well as the materials from which it is composed. The electronic and data acquisition (DAQ) systems are discussed, and performance of the ECal modules, as deduced from measurements with particle beams, cosmic rays, the calibration system, and T2K data, is described.
The T2K ND280 Off-Axis Pi-Zero Detector
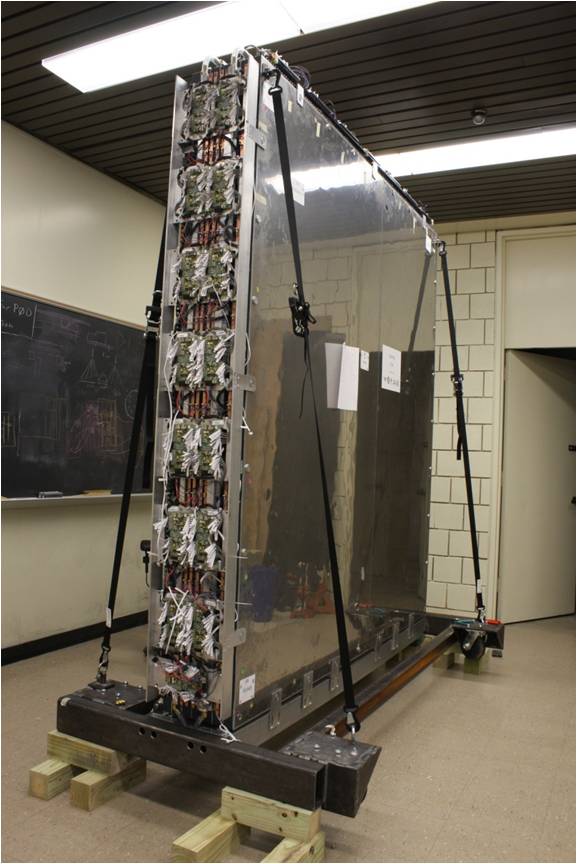

The Pi-Zero detector (PØD) is one of the subdetectors that makes up the off-axis near detector for the Tokai-to-Kamioka (T2K) long baseline neutrino experiment. The primary goal for the PØD is to measure the relevant cross sections for neutrino interactions that generate pi-zero’s, especially the cross section for neutral current pi-zero interactions, which are one of the dominant sources of background to the electron neutrino appearance signal in T2K. The PØD is composed of layers of plastic scintillator alternating with water bags and brass sheets or lead sheets and is one of the first detectors to use Multi-Pixel Photon Counters (MPPCs) on a large scale.
Optical transition radiation monitor for the T2K experiment
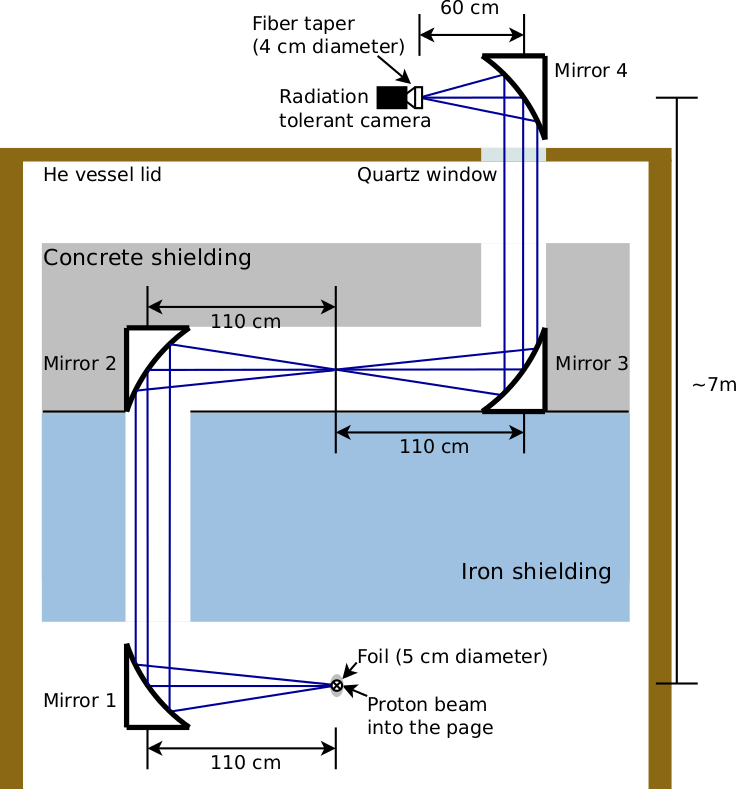
An optical transition radiation monitor has been developed for the proton beam-line of the T2K long base-line neutrino oscillation experiment. The monitor operates in the highly radioactive environment in proximity to the T2K target. It uses optical transition radiation, the light emitted from a thin metallic foil when the charged beam passes through it, to form a two-dimensional image of the 30 GeV proton beam profile in the transverse plane. One of its key features is an optical system capable of transporting the light over a large distance out of the harsh environment near the target to a lower radiation area where it is possible to operate a camera to capture this light. The monitor measures the proton beam position and width with an accuracy better than 0.5 mm, meeting the physics requirements of the T2K experiment.
The T2K Side Muon Range Detector (SMRD)
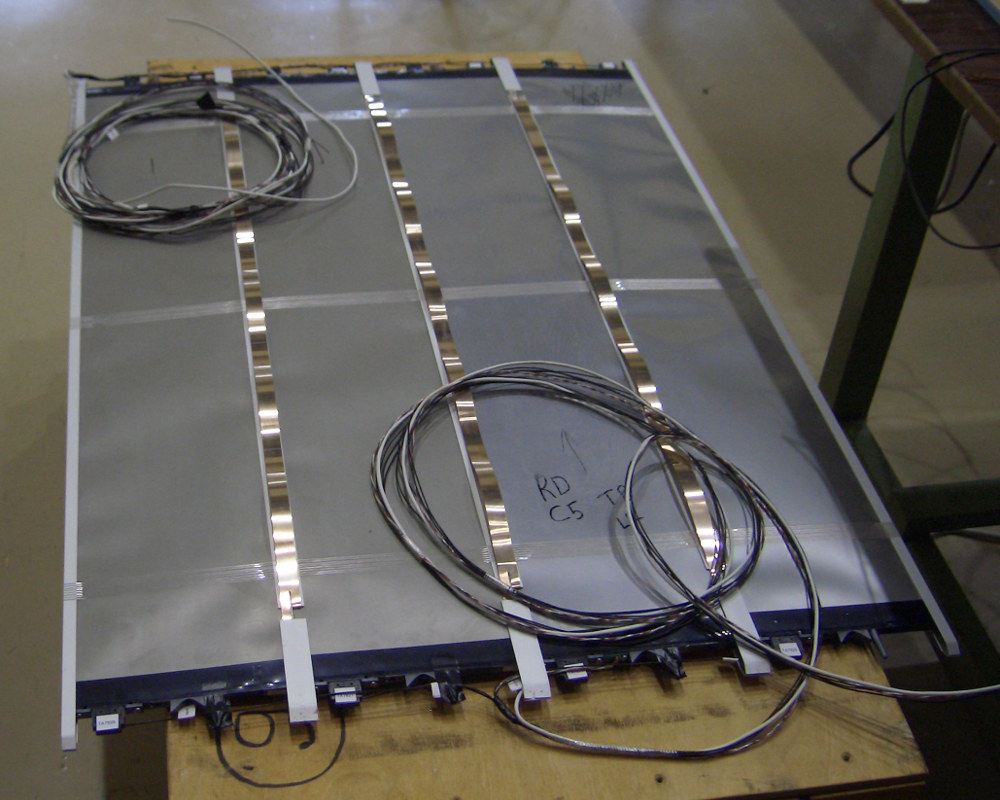
The near detectors include a magnetized off-axis detector (ND280) which measures the unoscillated neutrino flux and neutrino cross-sections. The present paper describes the outermost component of ND280 which is a Side Muon Range Detector (SMRD) composed of scintillation counters with embedded wavelength shifting fibers and Multi-Pixel Photon Counter readout. The components, performance and response of the SMRD are presented.
The T2K Fine-Grained Detectors
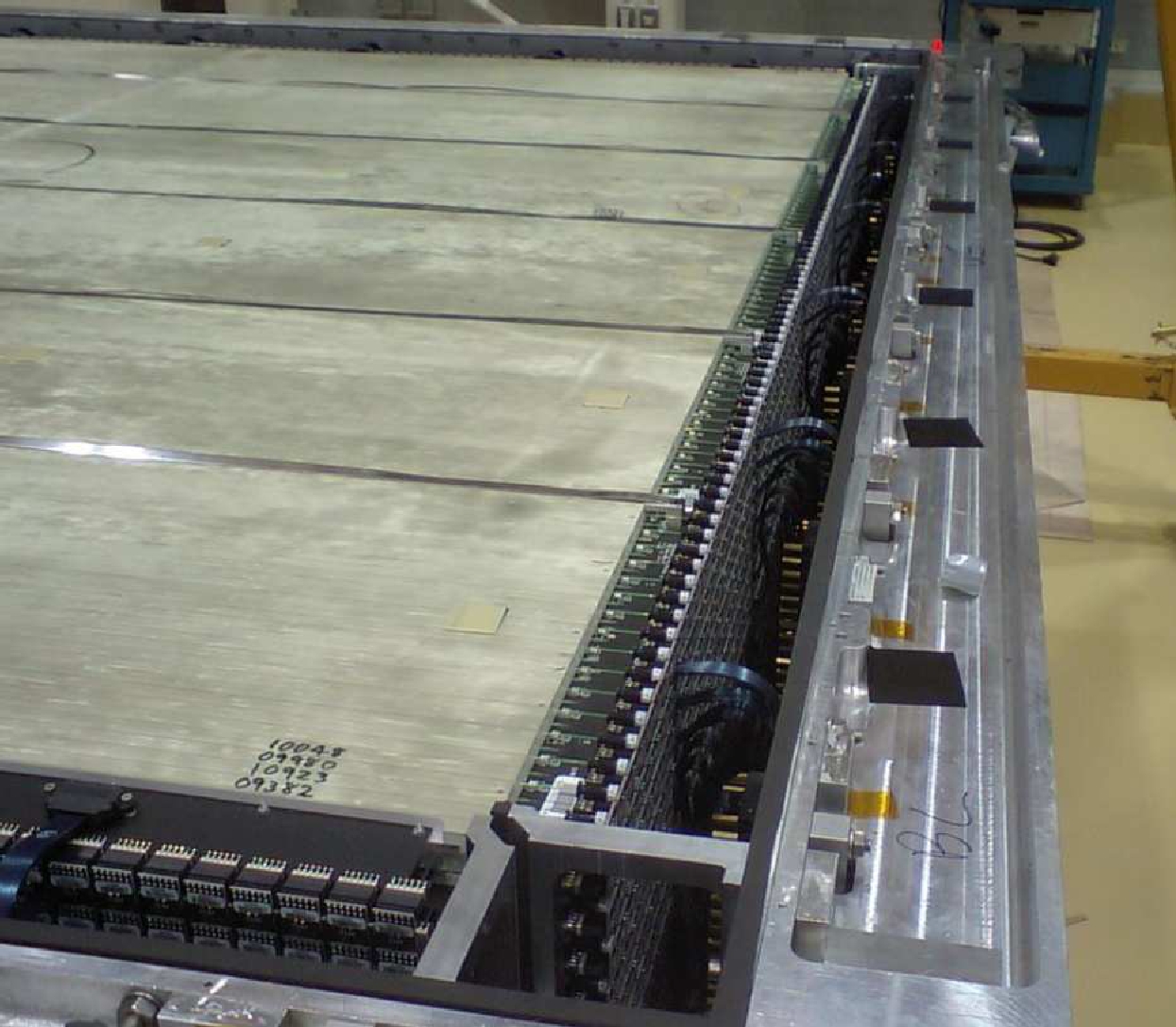

This paper describes the design and construction of two massive fine-grained detectors (FGDs) that serve as active targets in the ND280 tracker. One FGD is composed solely of scintillator bars while the other is partly scintillator and partly water. Each element of the FGDs is described, including the wavelength shifting fiber and Multi-Pixel Photon Counter used to collect the light signals, the readout electronics, and the calibration system. Initial tests and in situ results of the FGDs’ performance are also presented.
Measurements of the T2K neutrino beam properties using the INGRID on-axis near detector
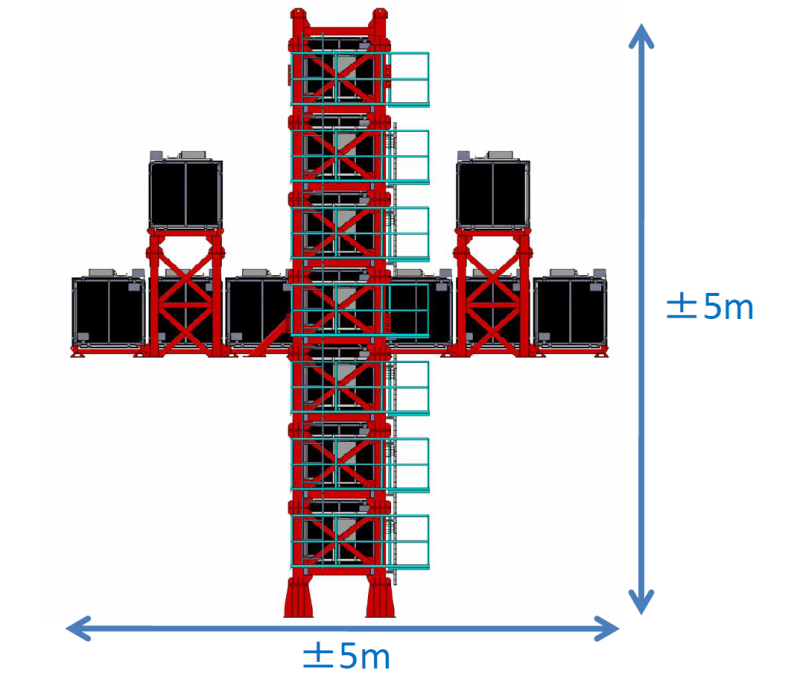
Precise measurement of neutrino beam direction and intensity was achieved based on a new concept with modularized neutrino detectors. INGRID (Interactive Neutrino GRID) is an on-axis near detector for the T2K long baseline neutrino oscillation experiment. INGRID directly monitors the muon neutrino beam profile center and intensity using the number of observed neutrino events in each module. The neutrino beam direction is measured with accuracy better than 0.4 mrad from the measured profile center. The normalized event rate is measured with 4% precision.
Design and performance of the muon monitor for the T2K neutrino oscillation experiment
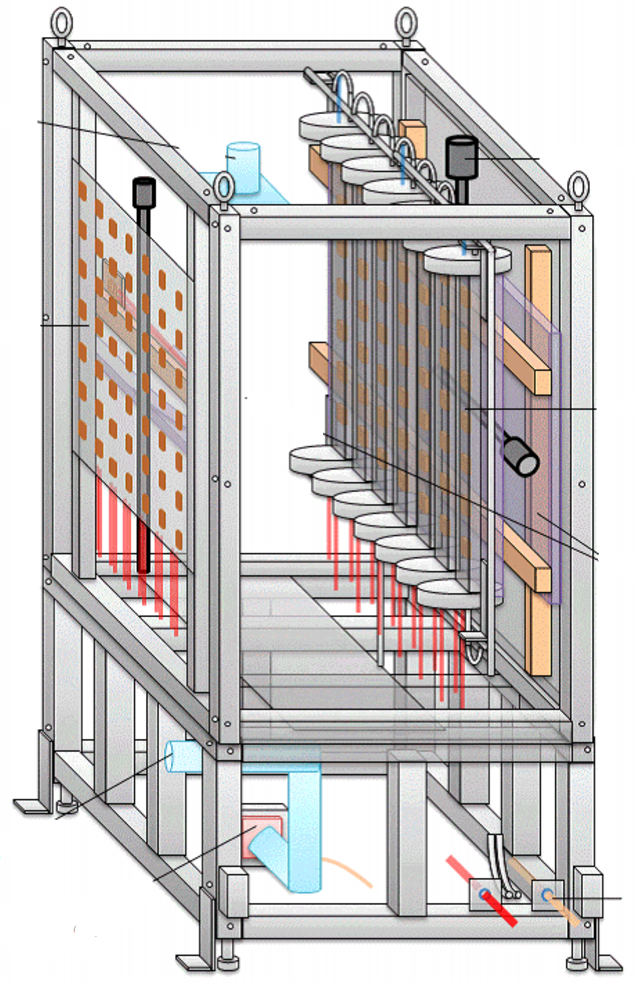
This article describes the design and performance of the muon monitor for the T2K (Tokaito-Kamioka) long baseline neutrino oscillation experiment. The muon monitor consists of two types of detector arrays: ionization chambers and silicon PIN photodiodes. It measures the intensity and profile of muons produced, along with neutrinos, in the decay of pions. The measurement is sensitive to the intensity and direction of the neutrino beam.
Time projection chambers for the T2K near detectors
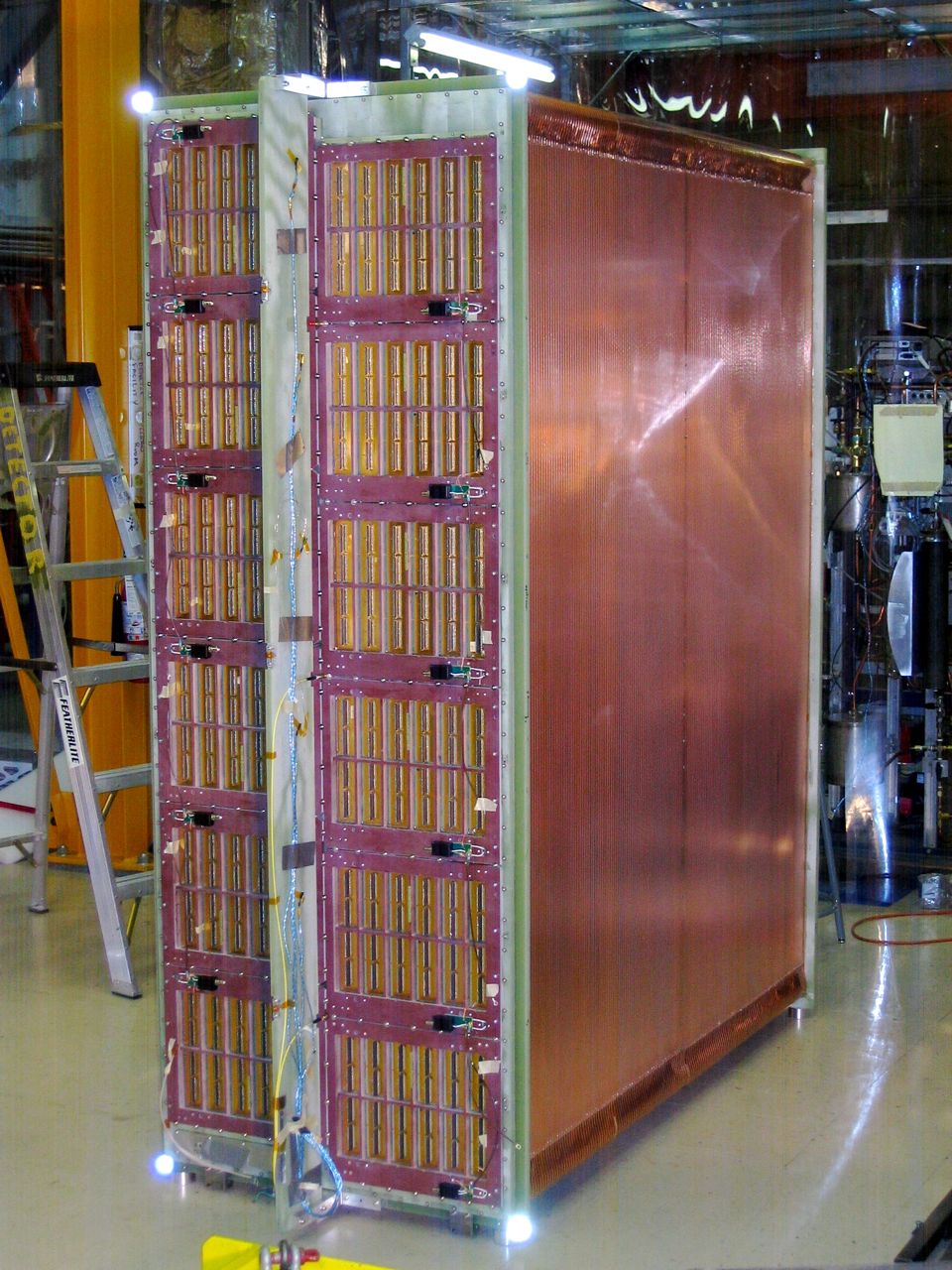

A key element of the near detectors is the ND280 tracker, consisting of two active scintillator-bar target systems surrounded by three large time projection chambers (TPCs) for charged particle tracking.
This paper describes the design and construction of the TPCs, the micromegas modules, the readout electronics, the gas handling system, and shows the performance of the TPCs as deduced from measurements with particle beams, cosmic rays, and calibration system.
The T2K Experiment
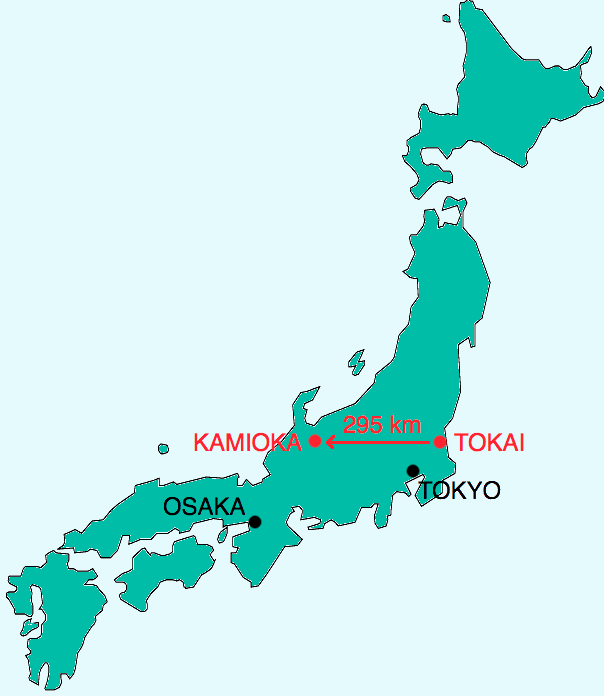
This paper provides a comprehensive review of the instrumentation aspect of the T2K experiment and a summary of the vital information for each subsystem.


