Search for Electron Antineutrino Appearance in a Long-baseline Muon Antineutrino Beam
Electron antineutrino appearance is measured by the T2K experiment in an accelerator-produced antineutrino beam, using additional neutrino beam operation to constrain parameters of the Pontecorvo-Maki-Nakagawa-Sakata (PMNS) mixing matrix. T2K observes 15 candidate electron antineutrino events with a background expectation of 9.3 events. Including information from the kinematic distribution of observed events, the hypothesis of no electron antineutrino appearance is disfavored with a significance of 2.40σ and no discrepancy between data and PMNS predictions is found. A complementary analysis that introduces an additional free parameter which allows non-PMNS values of electron neutrino and antineutrino appearance also finds no discrepancy between data and PMNS predictions.
arXiv preprint: https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.07283
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.161802
Reference: Phys.Rev.Lett. 124 (2020) 16, 161802
Measurements of νμ-bar and νμ-bar+νμ charged-current cross-sections without detected pions or protons on water and hydrocarbon at a mean anti-neutrino energy of 0.86 GeV
We report measurements of the flux-integrated |νμ-bar| and |νμ-bar+| charged-current cross-sections on water and hydrocarbon targets using the T2K anti-neutrino beam with a mean beam energy of 0.86 GeV. The signal is defined as the (anti-)neutrino charged-current interaction with one induced || and no detected charged pion or proton. These measurements are performed using a new WAGASCI module recently added to the T2K setup in combination with the INGRID Proton Module.
Improved constraints on neutrino mixing from the T2K experiment with 3.13×10E21 protons on target
The T2K experiment reports updated measurements of neutrino and antineutrino oscillations using both appearance and disappearance channels. This result comes from an exposure of 14.9(16.4)×10E20 protons on target in neutrino (antineutrino) mode. Significant improvements have been made to the neutrino interaction model and far detector reconstruction. An extensive set of simulated data studies have also been performed to quantify the effect interaction model uncertainties have on the T2K oscillation parameter sensitivity. T2K performs multiple oscillation analyses that present both frequentist and Bayesian intervals for the Pontecorvo-Maki-Nakagawa-Sakata parameters. For fits including a constraint on sin2θ13 from reactor data and assuming normal mass ordering T2K measures sin2θ23=0.53-0.04+0.03 and Δm322=(2.45±0.07)×10-3 eV2 c-4. The Bayesian analyses show a weak preference for normal mass ordering (89% posterior probability) and the upper sin2θ23 octant (80% posterior probability), with a uniform prior probability assumed in both cases. The T2K data exclude CP conservation in neutrino oscillations at the 2σ level.
First T2K measurement of transverse kinematic imbalance in the muon-neutrino charged-current single-π+ production channel containing at least one proton
This paper reports the first T2K measurement of the transverse kinematic imbalance in the single- production channel of neutrino interactions. We measure the differential cross sections in the muon-neutrino charged-current interaction on hydrocarbon with a single- and at least one proton in the final state, at the ND280 off-axis near detector of the T2K experiment. The extracted cross sections are compared to the predictions from different neutrino-nucleus interaction event generators. Overall, the results show a preference for models which have a more realistic treatment of nuclear medium effects including the initial nuclear state and final-state interactions.
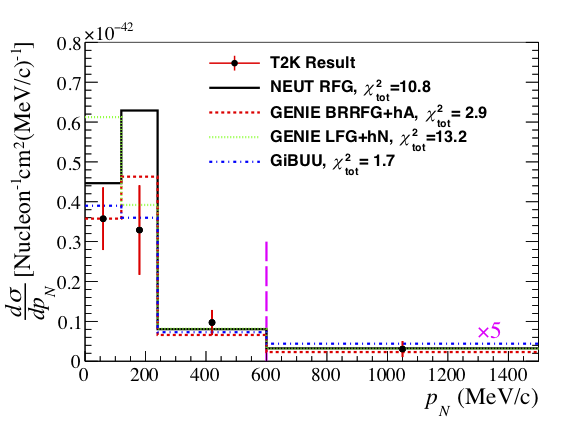
Simultaneous measurement of the muon neutrino charged-current cross section on oxygen and carbon without pions in the final state at T2K
This paper reports the first simultaneous measurement of the double differential muon neutrinocharged-current cross section on oxygen and carbon without pions in the final state as a function ofthe outgoing muon kinematics, made at the ND280 off-axis near detector of the T2K experiment. The ratio of the oxygen and carbon cross sections is also provided to help validate various models’ability to extrapolate between carbon and oxygen nuclear targets, as is required in T2K oscillationanalyses. The data are taken using a neutrino beam with an energy spectrum peaked at 0.6 GeV.The extracted measurement is compared with the prediction from different Monte Carlo neutrino-nucleus interaction event generators, showing particular model separation for very forward-goingmuons. Overall, of the models tested, the result is best described using Local Fermi Gas descriptionsof the nuclear ground state with RPA suppression.
T2K measurements of muon neutrino and antineutrino disappearance using 3.13E21 protons on target
We report measurements by the T2K experiment of the parameters θ23 and Δm322, which govern the disappearance of muon neutrinos and antineutrinos in the three-flavor PMNS neutrino oscillation model at T2K’s neutrino energy and propagation distance. Utilizing the ability of the experiment to run with either a mainly neutrino or a mainly antineutrino beam, muon-like events from each beam mode are used to measure these parameters separately for neutrino and antineutrino oscillations. Data taken from 1.49×1021 protons on target (POT) in neutrino mode and 1.64×1021 POT in antineutrino mode are used. The best-fit values obtained by T2K were sin2(θ23)=0.51-0.07+0.06(0.43-0.05+0.21) and Δm322=2.47-0.09+0.08(2.50-0.13+0.18)×10-3 eV2/c4 for neutrinos (antineutrinos). No significant differences between the values of the parameters describing the disappearance of muon neutrinos and antineutrinos were observed. An analysis using an effective two-flavor neutrino oscillation model where the sine of the mixing angle is allowed to take nonphysical values larger than 1 is also performed to check the consistency of our data with the three-flavor model. Our data were found to be consistent with a physical value for the mixing angle.
First Measurement of the Charged Current antinumu Double Differential Cross Section on a Water Target without Pions in the final state
This paper reports the first differential measurement of the charged-current muon-antineutrino interaction cross section on water with no pions in the final state. The unfolded flux-averaged measurement using the T2K off-axis near detector is given in double-differential bins of μ+ momentum and angle. The integrated cross section in a restricted phase space is σ=(1.11±0.18)×10E−38 cm2 per water molecule. Comparisons with several nuclear models are also presented.
Constraint on the matter–antimatter symmetry-violating phase in neutrino oscillations
Nature Nature 580, 339–344 (2020)
The charge-conjugation and parity-reversal (CP) symmetry of fundamental particles is a symmetry between matter and antimatter. Violation of this CP symmetry was first observed in 19641, and CP violation in the weak interactions of quarks was soon established2. Sakharov proposed3 that CP violation is necessary to explain the observed imbalance of matter and antimatter abundance in the Universe. However, CP violation in quarks is too small to support this explanation. So far, CP violation has not been observed in non-quark elementary particle systems. It has been shown that CP violation in leptons could generate the matter–antimatter disparity through a process called leptogenesis4. Leptonic mixing, which appears in the standard model’s charged current interactions5,6, provides a potential source of CP violation through a complex phase δCP, which is required by some theoretical models of leptogenesis7,8,9. This CP violation can be measured in muon neutrino to electron neutrino oscillations and the corresponding antineutrino oscillations, which are experimentally accessible using accelerator-produced beams as established by the Tokai-to-Kamioka (T2K) and NOvA experiments10,11. Until now, the value of δCPhas not been substantially constrained by neutrino oscillation experiments. Here we report a measurement using long-baseline neutrino and antineutrino oscillations observed by the T2K experiment that shows a large increase in the neutrino oscillation probability, excluding values of δCP that result in a large increase in the observed antineutrino oscillation probability at three standard deviations (3σ). The 3σ confidence interval for δCP, which is cyclic and repeats every 2π, is [−3.41, −0.03] for the so-called normal mass ordering and [−2.54, −0.32] for the inverted mass ordering. Our results indicate CP violation in leptons and our method enables sensitive searches for matter–antimatter asymmetry in neutrino oscillations using accelerator-produced neutrino beams. Future measurements with larger datasets will test whether leptonic CP violation is larger than the CP violation in quarks.

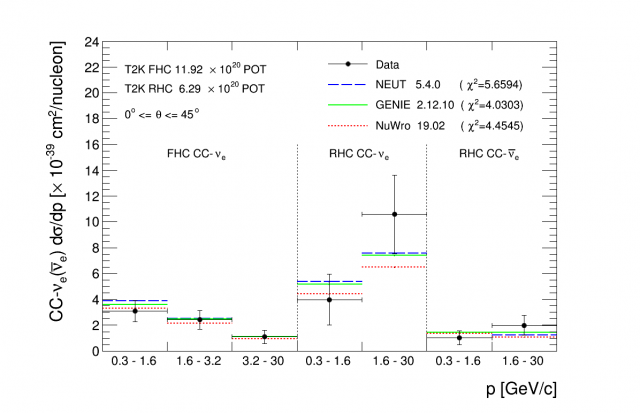
Measurement of the charged-current electron (anti-)neutrino inclusive cross-sections at the T2K off-axis near detector ND280
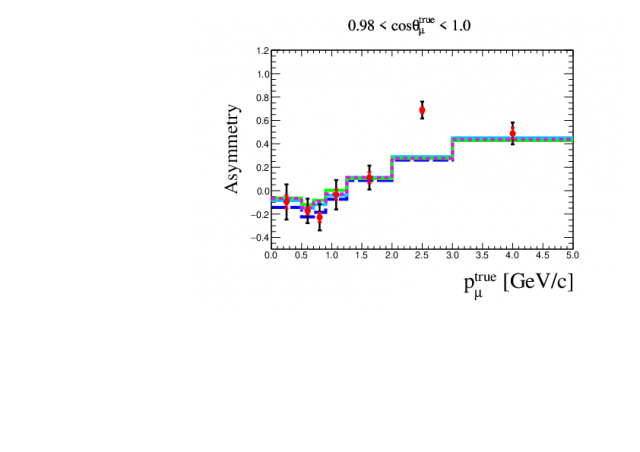
First combined measurement of the muon neutrino and antineutrino charged-current cross section without pions in the final state at T2K
This paper presents the first combined measurement of the double-differential muon neutrino and antineutrino charged-current cross sections with no pions in the final state on hydrocarbon at the off-axis near detector of the T2K experiment. The data analyzed in this work comprise 5.8×1020 and 6.3×1020 protons on target in neutrino and antineutrino mode respectively, at a beam energy peak of 0.6 GeV. Using the two measured cross sections, the sum, difference and asymmetry were calculated with the aim of better understanding the nuclear effects involved in such interactions. The extracted measurements have been compared with the prediction from different Monte Carlo generators and theoretical models showing that the difference between the two cross sections have interesting sensitivity to nuclear effects. Data release can found